Deploy Nebari on AWS
Introduction
This guide is to help first-time users set up an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account specifically for the purpose of using and deploying Nebari at a production scale. In this guide we will walk you through the following steps:
- Introduction
- Sign up for Amazon Web Services
- Authentication
- Initializing Nebari
- Deploying Nebari
- Destroying Nebari
If you are already familiar to AWS services, feel free to skip this first step and jump straight to the Nebari authentication section of this guide.
Sign up for Amazon Web Services
This documentation assumes that you are already familiar with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and that you have prior knowledge regarding AWS billing and cost usage for Kubernetes related services.
If you are new to AWS, we advise you to first sign up for a free account to get a better understanding of the platform and its features. Please refer to Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) and Amazon EKS Prerequisites for more information on account types and prerequisites for managing Kubernetes clusters.
For a more detailed cost estimate, please also refer to our Conceptual guides for more information regarding the basic infrastructure provided by Nebari.
A Nebari deployment on AWS will NOT fall into free tier usage as some of its inner components will lead to additional charges. Therefore, we recommend that you check AWS pricing documentation or contact your
cloud administrator for more information. If you provision resources outside the free tier, you may be charged. We're not responsible for any charges you may incur if this
happens.
Authentication
In order for Nebari to make requests against the AWS API and create its infrastructure, an authentication method with the appropriate permissions will be required. The best way to do this is using an IAM user with suitable permissions for your AWS account and Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
As a best practice, do not use the AWS account root user for any task where it's not
required. Instead, create a new IAM user for each person that requires administrator access. Then make those users administrators by placing them into an "Administrators" user
group, to which you attach the AdministratorAccess managed policy.
If you are using an already existing IAM user, please refer to Managing access keys for IAM users for detailed information on how to manage your IAM user's access keys.
If it's your first time creating a new IAM user, please refer to Creating your first IAM admin user and user group for more information. Otherwise, see Creating an IAM user in your AWS account for more information on how to create an IAM user.
Follow these steps to set up your access keys and user accounts:
-
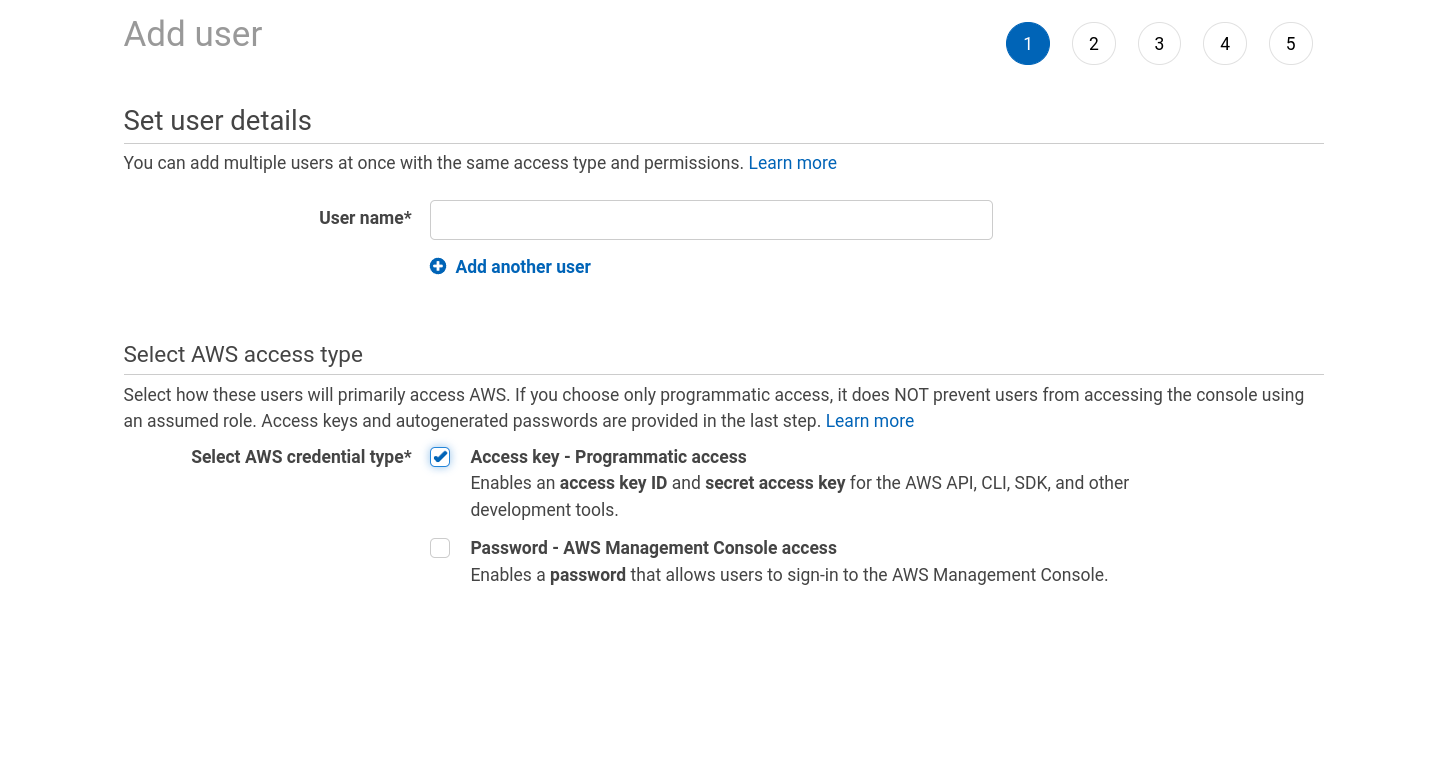
Go to IAM in your AWS Console, then Users, and Add Users;
-
Give the user a name, and tick Access Key - Programmatic access
-
Click Next
-
Select Attach existing policies directly, then select
AdministratorAccessfrom the list of policies. For more information, please refer to Policies and permissions in IAM; -
Then proceed with the new user creation setup.
Upon generation, the IAM role will provide a public Access Key ID and Secret Access Key. Download this file for reference later.
The Secret Access Key provides access to your AWS user account. It should be treated like any other secret credentials. In particular, it should never be checked into source control.
By default, Nebari will try to use the credentials associated with the current AWS infrastructure/environment for authentication. Please keep in mind that Nebari will only use these credentials to create the first roles and stricter permissions for Nebari's internal components. Refer to [Conceptual guides] for more information on how Nebari's components are secured.
Provide authentication credentials to Nebari by setting the following environment variables:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="Access Key ID"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="Secret Access Key"
These environment variables will apply only to your current shell session. If you want the variables to apply to future shell sessions also, set the variables in your shell
startup file (for example, for example in the ~/.bashrc or ~/.profile for the bash shell). You can also opt for direnv as a shell extension for managing your environment variables.
The steps in the following sections assume you have (i) completed the Install Nebari section, (ii) confirmed that Nebari is successfully installed in your environment, (iii) opted for AWS as your cloud provider, and (iv) already configured the Nebari environment variables. If you had any issues during the installation, please visit the "Get started" section of our troubleshooting page for further guidance.
Initializing Nebari
Great, you’ve gone through the Nebari installation and authentication setup steps, and have ensured that all the necessary environment variables have been properly set.
In the following steps you will be asked to provide a name for your project. This name will be used to generate the name of the infrastructure components that will be created in your AWS account. This name must comply with the following rules:
- Must be between 3-47 characters in length;
- Must begin with an alphanumeric character, and must only contain alphanumeric lowercase characters, dashes, and underscores;
- The name cannot start with
AWSoraws.
Those rules are enforced by the AWS Terraform Provider and are not configurable.
In this step, you'll run nebari init to create the nebari-config.yaml file.
-
In your terminal, start by creating a new project folder. For this demonstration, we will name the new folder
nebari-aws:mkdir nebari-aws && cd nebari-aws
-
Executing the
nebari init --guided-initcommand prompts you to respond to a set of questions, which will be used to generate thenebari-config.yamlfile with an infrastructure based on AWS.nebari init --guided-init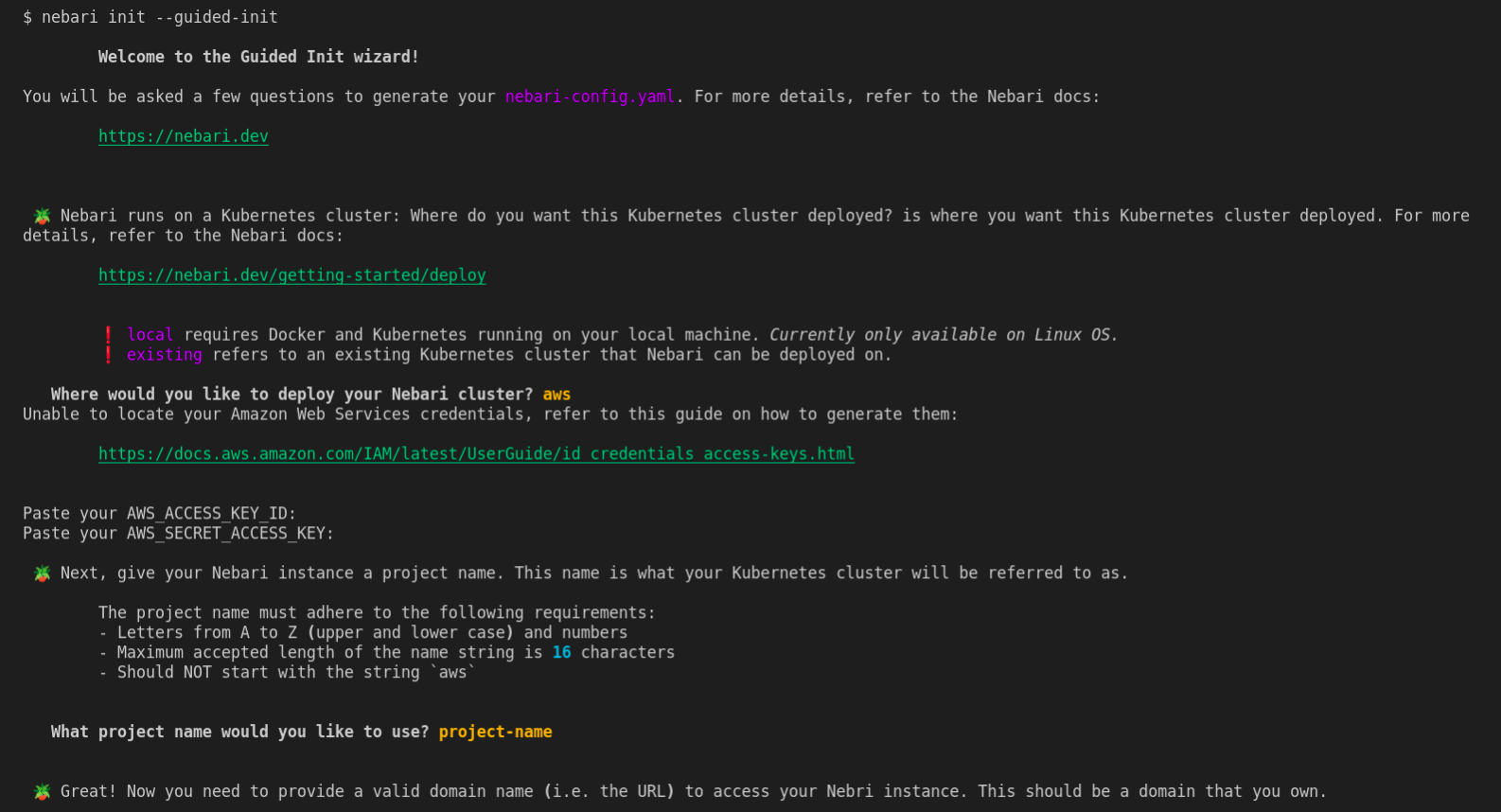
If you prefer not using the guided-init command then you can directly run the init command.
Executing the command below will generate a basic config file with an infrastructure based on AWS.
projectnamewill be the name of the folder/repo that will manage this Nebari deployment (it will be created).domainwill be the domain endpoint for your Nebari instance.auth-providersets your authentication provider that you plan to use inside of Keycloak, options are Github, Auth0, and password.
For this example, we'll run with project name projectname, endpoint domain domain, and with the authentication mode set to password. These can be updated later by directly modifying the nebari-config.yaml.
nebari init aws --project projectname \
--domain domain \
--auth-provider password
You will be prompted to enter values for some choices above if they are absent from the command line arguments (for example, project name and domain)
Nebari can also be deployed into an AWS GovCloud account, you simply need to ensure you specify the appropriate AWS GovCloud region in the amazon_web_services.region field of your nebari-config.yaml.
Once nebari init is executed, you should then be able to see the following output:
Securely generated default random password=*** for Keycloak root user stored at path=/tmp/QHUB_DEFAULT_PASSWORD
Congratulations, you have generated the all important nebari-config.yaml file 🎉
You can always make changes to your nebari-config.yaml file by editing the file directly.
If you do make changes to it you can ensure its still a valid configuration by running:
nebari validate --config path/to/nebari-config.yaml
For reference, if the previous Guided Init answers were converted into a direct nebari init command, it would be:
nebari init <cloud-provider> --project-name <project-name> --domain-name <domain-name> --namespace dev --auth-provider password
You can now deploy your Nebari instance with:
nebari deploy -c nebari-config.yaml
For more information, run nebari deploy --help or check out the documentation: https://www.nebari.dev/how-tos/
The main temp folder on a MacOS system can be found by inspecting the value of $TMPDIR. This folder and its files are not meant to be user-facing and will present you
with a seemingly random directory path similar to /var/folders/xx/xxxxx/T
You can see that Nebari is generating a random password for the root user of Keycloak. This password is stored in a temporary file and will be used to authenticate to the Keycloak server once Nebari's infrastructure is fully deployed, to create the first user accounts for administrator(s).
The Nebari initialization scripts create a nebari-config.yaml file that contains a collection of default preferences and settings for your deployment.
The generated nebari-config.yaml is the configuration file that will determine how the cloud infrastructure and Nebari is built and deployed in the next step. Since it is a
plain text file, you can edit it manually if you are unhappy with the choices you made during initialization, or delete it and start over again by re-running nebari init/nebari init --guided-init.
Deploying Nebari
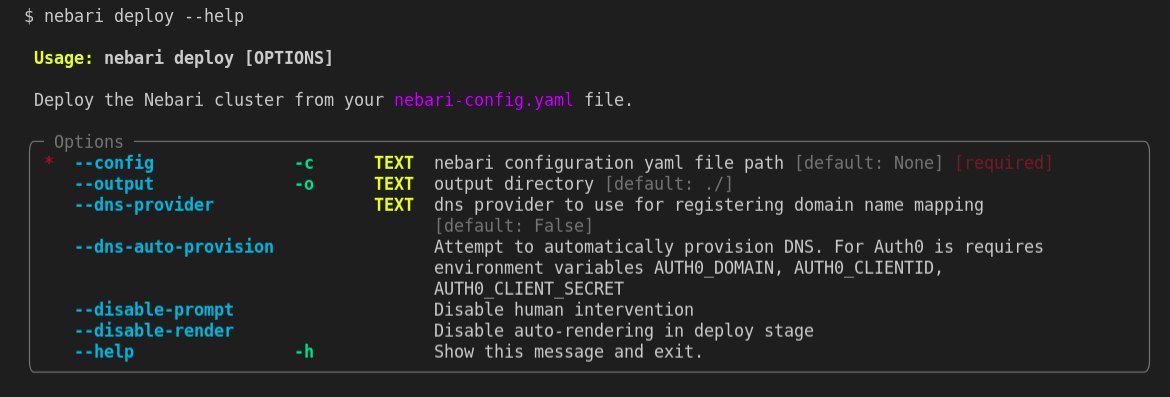
To see all the options available for the deploy command, run the following command:
nebari deploy --help
With the nebari-config.yaml configuration file now created, Nebari can be deployed for the first time. Type the following command on your command line:
nebari deploy -c nebari-config.yaml
During deployment, Nebari will require you to set a DNS record for the domain defined during initialize. Follow the instructions on How to set a DNS record for Nebari for an overview of the required steps.
The terminal will prompt you to press enter to check the authentication credentials that were added as part of the preceding nebari init command. Once Nebari is
authenticated, it will start its infrastructure deployment process, which will take a few minutes to complete.
If the deployment is successful, you will see the following output:
[terraform]: Nebari deployed successfully
Services:
- argo-workflows -> https://projectname.domain/argo/
- conda_store -> https://projectname.domain/conda-store/
- dask_gateway -> https://projectname.domain/gateway/
- jupyterhub -> https://projectname.domain/
- keycloak -> https://projectname.domain/auth/
- monitoring -> https://projectname.domain/monitoring/
Kubernetes kubeconfig located at file:///tmp/NEBARI_KUBECONFIG
Kubecloak master realm username=root *****
...
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed Nebari on AWS! From here, see Initial Nebari Configuration for instructions on the first steps you should take to prepare your Nebari instance for your team's use.
Destroying Nebari
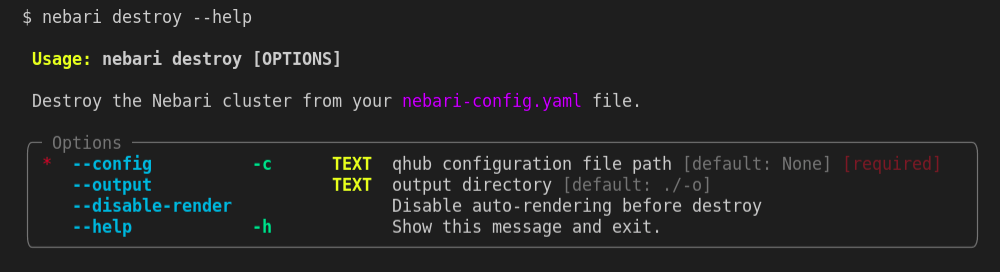
To see all the options available for the destroy command, type the following command on your command line:
nebari destroy --help
Nebari also has a destroy command that works the same way the deploy works but instead of creating the provisioned resources it destroys it.
nebari destroy -c nebari-config.yaml